为什么要使用 Redis 集群
这种模型实际上也是一种 Redis 集群,优点如下:
- 实现数据的冗余备份
- 基于故障转移,可以保证一定程度的可用性
- 读写分离,提高整体读取性能
但是,这种模型存在一个严重的问题:只有一个主节点,所有的写请求都是直接发到主节点上,主节点压力很大,如果写请求 QPS 很高,很有可能导致主节点撑不住,然后挂掉
针对这种情况,Redis 原生 支持了 Redis 集群模式(Redis Cluster),这种模式往往有多个主节点,并且每个主节点还有一些从节点来保证可用性
下面的文章,会基于 Redis 官方文档 来简要介绍 Redis 集群
Redis 集群实现了什么功能
- High performance and linear scalability up to 1000 nodes. There are no proxies, asynchronous replication is used, and no merge operations are performed on values.
- Acceptable degree of write safety: the system tries (in a best-effort way) to retain all the writes originating from clients connected with the majority of the master nodes. Usually there are small windows where acknowledged writes can be lost. Windows to lose acknowledged writes are larger when clients are in a minority partition.
- Availability: Redis Cluster is able to survive partitions where the majority of the master nodes are reachable and there is at least one reachable replica for every master node that is no longer reachable. Moreover using replicas migration, masters no longer replicated by any replica will receive one from a master which is covered by multiple replicas.
简单来说,Redis Cluster 实现了:
- 高性能:支持扩展至高 1k+ 节点
- 写入安全保障:在保证性能的同时,有一定的写入安全保障(可能会丢失一部分数据)
- 高可用:基于副本迁移,只要有足够的从节点,Redis 集群能保证服务的可用性
但是,在 Cluster 模式下,Redis 不支持 select 操作,这意味着只能有 DB0
在 Redis Cluster 协议下,Server 与 Client 在 Redis 集群中的身份
To perform their tasks all the cluster nodes are connected using a TCP bus and a binary protocol, called the Redis Cluster Bus. Every node is connected to every other node in the cluster using the cluster bus. Nodes use a gossip protocol to propagate information about the cluster in order to discover new nodes, to send ping packets to make sure all the other nodes are working properly, and to send cluster messages needed to signal specific conditions. The cluster bus is also used in order to propagate Pub/Sub messages across the cluster and to orchestrate manual failovers when requested by users (manual failovers are failovers which are not initiated by the Redis Cluster failure detector, but by the system administrator directly)
Server 与 Client 之间,通过基于 TCP 的 Redis Serialization Protocol 协议建立连接
而所有的 Cluster 节点之间,通过 Cluster Bus 连接,节点之间使用 gossip 协议通信,目的是为了:
- 发现新节点
- 检测彼此的健康状态(服务是否可用)
- 在节点间发送信号,提供所需的集群消息
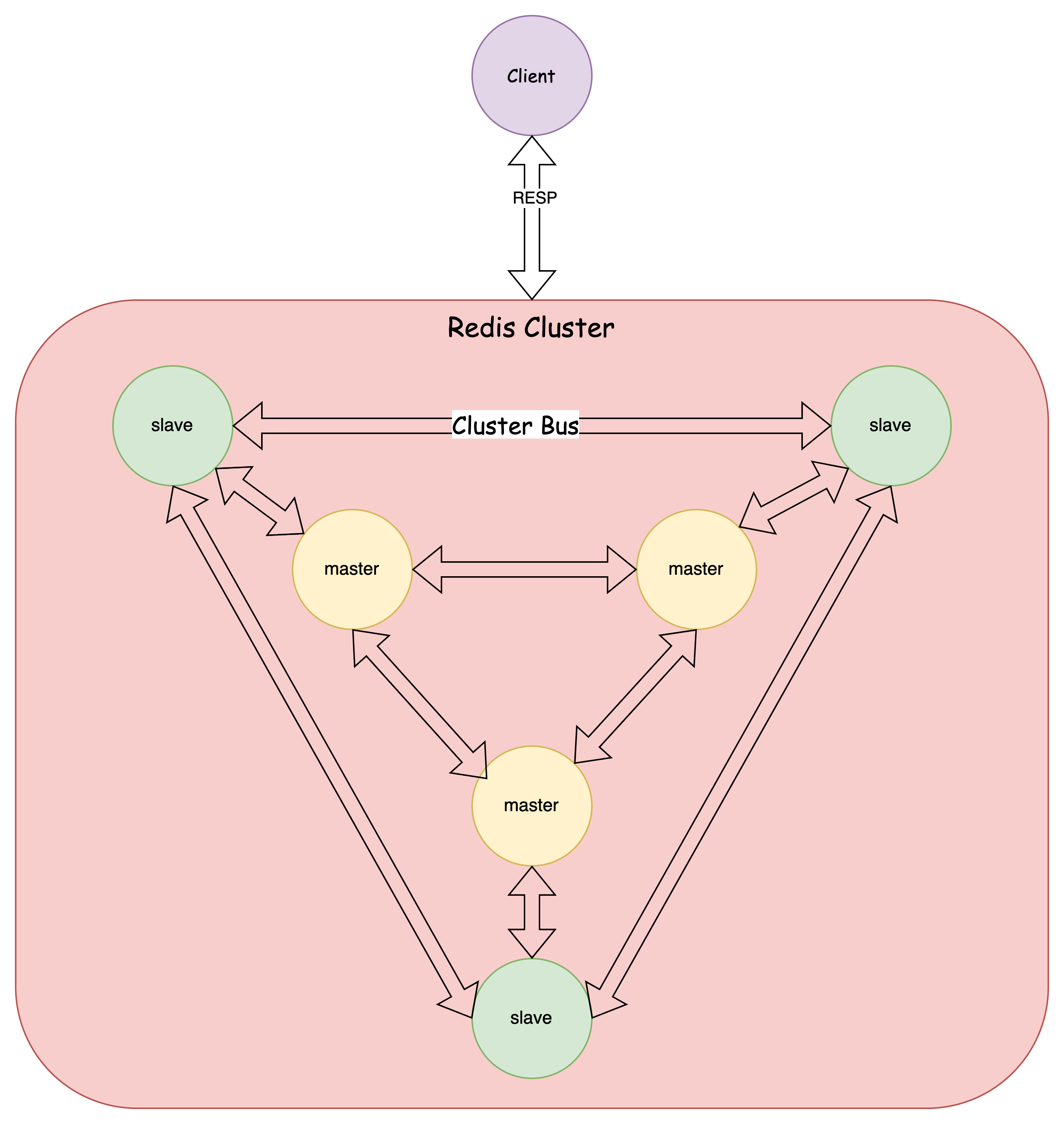
每个节点都要与其它节点建立 TCP 连接,应该是 5 条边才对
这里的图片,为了看起来不太乱,每个节点都少画了两条边
The client is in theory free to send requests to all the nodes in the cluster, getting redirected if needed, so the client is not required to hold the state of the cluster. However clients that are able to cache the map between keys and nodes can improve the performance in a sensible way.
客户端向 Redis 集群发送读写请求时,只需要连接任意一个节点,如果要操作的数据不在这个节点上,请求会被重定向到目标节点上
当然,为了避免重定向的性能开销,Redis 的客户端会在建立连接时,将数据与节点的映射关系缓存到本地
如何减少数据丢失
Writes targeting the minority side of a partition have a larger window in which to get lost. For example, Redis Cluster loses a non-trivial number of writes on partitions where there is a minority of masters and at least one or more clients, since all the writes sent to the masters may potentially get lost if the masters are failed over in the majority side.
- 一种情况就是在主节点向从节点同步增量数据时,主节点挂了,导致的数据丢失,比较随机,不太好避免
- 还有一种情况就是常说的「脑裂」现象,即由于网络问题,集群内其它节点误认为主节点挂了
于是执行故障转移,选出新的主节点,此时就有两个主节点了(当然,原先的主节点由于网络问题,无法感知)
等到原先的主节点的网络恢复以后,集群会以为原先的主节点上线了,于是让原先的主节点降级为新的主节点的从节点
那么数据丢失发生在哪里呢?
集群误认为主节点宕机,这个过程是需要时间的
对客户端来说,此时是不知道集群内部网络不好的,还是会正常发送写请求
假设主节点收到了这些写请求,肯定要同步给从节点,但由于内部网络问题,无法完成同步
如果内部网络迟迟不恢复,那么在完成同步之前,就选出了新的主节点,原来的主节点降级后,这部分增量数据就会丢失
如何减少数据丢失?
Redis 是这样做的:
Specifically, for a master to be failed over it must be unreachable by the majority of masters for at least NODE_TIMEOUT, so if the partition is fixed before that time, no writes are lost. When the partition lasts for more than NODE_TIMEOUT, all the writes performed in the minority side up to that point may be lost. However the minority side of a Redis Cluster will start refusing writes as soon as NODE_TIMEOUT time has elapsed without contact with the majority, so there is a maximum window after which the minority becomes no longer available.
可以调整 NODE_TIMEOUT 参数
假设集群检测到主节点疑似宕机的时间为 t0,主节点恢复时间为 t1
- 如果 t1 在 t0 +
NODE_TIMEOUT前,那么不会有数据丢失,因为不会选举新的主节点 - 否则,根据与从节点的同步情况,会丢失未同步给所有从节点的增量数据
高可用
Redis Cluster 有 故障转移 的能力
这个故障转移的过程与 基于哨兵的故障转移 过程很类似
以 5 主 5 从(即每一个主节点都有一个从节点)为例,假设掉了两个节点,那么只有:
- 掉了一个主节点
- 该主节点的从节点也挂了
这种情况,整个 Redis Cluster 服务才会不可用,概率为 (5*2)/(10*9) = 11%
当然如果是 5 主 6 从(即有一个主节点具有两个从节点),情况就不一样了
Thanks to a Redis Cluster feature called replicas migration the Cluster availability is improved in many real world scenarios by the fact that replicas migrate to orphaned masters (masters no longer having replicas).
So at every successful failure event, the cluster may reconfigure the replicas layout in order to better resist the next failure.
Redis 引入了 副本迁移 机制,在检测到 孤儿主节点 时会触发,将其它主节点的部分从节点迁移到孤儿主节点,进一步保证可用性
高性能
Very high performance and scalability while preserving weak but reasonable forms of data safety and availability is the main goal of Redis Cluster.
Redis 集群的主要目标是在保持数据安全性和可用性的同时,提供非常高的性能和可伸缩性。进一步的,以下几个因素保证了 Redis Cluster 的高性能:
- 客户端缓存 key 与 node 的关系
- 异步复制
- 线性扩展能力(n 个主节点的集群的性能,可以看作单个主节点性能的 n 倍)
客户端缓存 key 与 node 的关系
任意 Redis Cluster 节点收到 Client 的请求后:
- 检查这个 key 的 value 是否在本节点上,如果在,那就由自己处理
- 否则,将客户端的请求正确重定向到目标节点
为了提高性能,客户端会在本地缓存 key 与 node 的映射关系(即一个哈希表),具体来说:
- key:hash slots
- value:<node_ip, node_port>
例如,假设 clusterA 负责 hash slots 在 (114, 514) 的数据,那么客户端就会缓存像这样的内容:
- key:114 ~ 514
- value:<cluterA’s IP, cluterA’s Port>
那么,客户端在发起请求前,会先计算 key 对应的 hash slots,然后请求对应的节点,避免一次重定向
当然,这个缓存可能会过期,此时就还是要依赖 cluster 的重定向了
Redis 集群的基本组件
Key distribution model
实现数据的分片,依赖的就是 key 分发模型
Redis 给整个集群分配了 16384 个哈希槽(hash slots),每个 cluster 节点都拥有一部分 hash slots
确定 key 在哪个 hash slot,这个过程使用 CRC16 算法,具体来说:
hash_slot = CRC16(key) % 16384
在客户端读写数据时:
- 先计算出 hash slot
- 读取本地缓存,获取这个 hash slot 在哪个 cluster 节点上存储
- 请求对应的 cluster 节点
cluster 节点收到数据后:
- 校验一下这个 key 是否在当前 cluster 节点
- 如果在,那么处理客户端的请求即可
- 如果不在,读取本地缓存,确定这个 hash slot 在哪个 cluster 节点上存储,并发送 MOVE 错误给客户端,以重定向到正确的 cluster 节点
Hash Tags
There is an exception for the computation of the hash slot that is used in order to implement hash tags. Hash tags are a way to ensure that multiple keys are allocated in the same hash slot. This is used in order to implement multi-key operations in Redis Cluster.
如果要存储一个 User 对象在 Redis 中,有可能像这样实现:
user:114514:name
user:114514:age
user:114514:sex
...
如果要获取一个 User 对象所有的成员的值,可能会这样做:
MGET user:114514:name, user:114514:age, user:114514:sex
如果这些 key 不在同一个 cluster 中,那么操作就很麻烦了
因此,为了 批量操作 key,就要使用 hash tags 了
Redis Cluster 可以保证拥有相同的 hash tags 的 key,永远具有相同的 hash slots,这意味着会存储在相同的 cluster 节点中
使用 hash tags 的语法如下:
{<key_prefix>}<key_suffix>
这样,在计算 key 所属的 hash slots 时,就只会计算 {} 内部的部分,即 CRC16(key_prefix) % 16384
对于上面的示例,可以这样设置 key:
{user:114514}.name
{user:114514}.age
{user:114514}.sex
Cluster 属性
redis-cli cluster nodes
d1861060fe6a534d42d8a19aeb36600e18785e04 127.0.0.1:6379 myself - 0 1318428930 1 connected 0-1364
3886e65cc906bfd9b1f7e7bde468726a052d1dae 127.0.0.1:6380 master - 1318428930 1318428931 2 connected 1365-2729
d289c575dcbc4bdd2931585fd4339089e461a27d 127.0.0.1:6381 master - 1318428931 1318428931 3 connected 2730-4095
可以看到,一个 cluster node 具有以下基本属性:
- 节点 id
- ip 和 port(或者 host)
- 身份:master or slave
- 该节点最后一次被 ping 的时间戳
- 该节点最后一次收到 pong 的时间戳
- config 的版本号
- 负责的 hash slots
Cluster bus
Cluster bus protocol: a binary protocol composed of frames of different types and sizes. Every node is connected to every other node in the cluster using the cluster bus.
Cluster bus 基于 gossip 协议,集群中,每个节点的通信通过 Cluster bus 进行
Cluster bus 的作用
Nodes use a gossip protocol to propagate information about the cluster in order to discover new nodes, to send ping packets to make sure all the other nodes are working properly, and to send cluster messages needed to signal specific conditions. The cluster bus is also used in order to propagate Pub/Sub messages across the cluster and to orchestrate manual failovers when requested by users (manual failovers are failovers which are not initiated by the Redis Cluster failure detector, but by the system administrator directly).
- 节点发现:集群节点使用集群总线来发现集群中的其他节点。
- 故障检测:集群总线用来交换定期的心跳消息,这些心跳包含故障检测消息,用于确定节点是否处于可达状态。
- 配置更新:当集群配置发生变化时(如节点加入或离开集群),通过集群总线传播这些变化。
- 投票和协商:在某些操作需要共识时(例如,当一个主节点无法达到时,选择一个副本来提升为新的主节点),集群总线用于投票和协商流程。
- 公共订阅/发布消息的传播:集群总线还用于在集群各节点中传播订阅/发布(pub/sub)消息。
总的来说,Cluster bus 就是提供一个 高效 的节点间交互方式
开放的端口
Cluster bus 开放的端口默认为 RESP 开放的端口 + 10000
举个例子,RESP,即 Cluster Node 与 Client 通信的端口默认为 6379,那么 Cluster bus 的端口就是 16379
当然,也可以手动指定 cluster bus 的端口,修改 cluster-port 即可
gossip 协议
Gossip 协议是一种在分布式系统中用于节点间通信的协议,它通过 流言蜚语(即 Gossiping)的方式来交换信息,从而实现信息的传播和一致性。
Gossip 协议与我们平常所说的流言传播相似,一个节点会 随机选择其他几个节点 分享信息,这些被选择的节点又会同样选择其他节点进行信息的传播,这样信息就 像病毒一样快速扩散开 来。
Gossip 的特点就是 去中心化,具有可伸缩性和鲁棒性
为什么 Redis Cluster bus 要使用 gossip 协议呢?
来看看 Redis 官方怎么说的:
While Redis Cluster nodes form a full mesh, nodes use a gossip protocol and a configuration update mechanism in order to avoid exchanging too many messages between nodes during normal conditions, so the number of messages exchanged is not exponential.
在一个大型集群中,如果节点需要以直接的方式交换状态信息或配置更新,那么每个节点都需要与其他每个节点进行通信。这意味着在 N 个节点的集群中,每个节点都需要发送 N-1 个消息来通知每个其他节点,总共就有 N*(N-1) 次通信。对于大型集群,这个数字会非常大,随着节点数目线性增加,需要的通信次数会以平方级别(N 的平方)增长
如果使用 gossip 协议,每个节点发送数据,仅仅会随机选择一些节点发送,然后慢慢传播开来,就像流言(病毒)传播一样,这样,整个集群内的消息数量处于一个可控范围,不会造成太大的压力
当然,gossip 协议存在 消息不及时 的缺点:消息在节点间传播是需要时间的,经过多个节点的转发,时效性不如直接发送好(不过大型集群,直接发送的压力太大,可能造成网络拥塞,时效性可能还不如 gossip)
重定向与重新分片
MOVED Redirection
前面提到了,如果客户端请求的数据不在某个 cluster 节点上,cluster 会给客户端发送重定向,告诉客户端应该请求哪个节点
事实上,重定向分为两种:
- 临时重定向
- 永久重定向
这里先说说永久重定向
永久重定向在 Redis Cluster 的语义为:该 key 的 hash slot 永久迁移到了另一个节点
永久重定向会发生在两种情况:
- 这个 hash slot 本来就不是由当前 cluster 节点负责
- 这个 hash slot 原本由当前 cluster 节点负责,但是由于某种原因,迁移到了另一个节点
cluster 节点发送永久重定向的过程:
- 发送 MOVED message,包含了新的 cluster 的 ip 和 port
- 发送 cluster node 到 hash slots 的 映射关系(哈希表)给客户端
客户端会更新(或者存储)映射关系到本地,并重新发起请求到正确的 cluster node
Resharding
添加一个节点的步骤:
- 添加一个新的节点:
redis-cli --cluster add-node <new_host:new_port> <existing_host:existing_port> - 分配散列插槽:
redis-cli --cluster reshard <host:port>其中,host:port 可以是集群中任意一个存在节点的 host:port
reshard 的示例输出如下:
$ redis-cli --cluster reshard 127.0.0.1:7000
>>> Performing Cluster Check (using node 127.0.0.1:7000)
M: 50ae0f1a7e203a3fbb1a76a8af04b3f398e2f1e4 127.0.0.1:7000
slots:[0-5460] (5461 slots) master
M: 2a0d96e5c41ac012b93c7c402769178d6ad8cfd3 127.0.0.1:7001
slots:[5461-10922] (5462 slots) master
M: b59c1b9f4557d17a6e6c9c4e0fd607a72bda5e60 127.0.0.1:7002
slots:[10923-16383] (5461 slots) master
How many slots do you want to move (from 1 to 16384)? 1000
What is the receiving node ID?
Please type "help" if you need help.
Node ID: 2a0d96e5c41ac012b93c7c402769178d6ad8cfd3
Please enter all the source node IDs.
Type 'all' to use all the nodes as source nodes for the hash slots.
Type 'done' once you entered all the nodes IDs and you want to start the rebalancing.
Source node #1:50ae0f1a7e203a3fbb1a76a8af04b3f398e2f1e4
done
Ready to move 1000 slots.
Source node: 50ae0f1a7e203a3fbb1a76a8af04b3f398e2f1e4
Destination node: 2a0d96e5c41ac012b93c7c402769178d6ad8cfd3
Moving slot 1234 from 127.0.0.1:7000 to 127.0.0.1:7001: DONE
...
...
Moving slot 1235 from 127.0.0.1:7000 to 127.0.0.1:7001: DONE
...
...
(Multiple lines indicating progress of slot migrations)
...
[OK] Done
可以看出,reshard 需要指定源 cluster node 和目标 cluster node,以及要迁移的 hash slot 的数量
哈希槽的重分配过程如下:
- 原节点设置为 MIGRATING 状态
- 新节点设置为 IMPORTING 状态
- 开始迁移哈希槽
- 迁移过程中,如果有新的客户端请求:
- 如果 key 存在,那么 在原节点执行
- 否则,原节点会将请求 重定向 到新的节点,在新的节点执行
- 迁移完成,新节点发送一个 OK 给原节点
- 原节点收到 OK 后,将迁移哈希槽的数据从本地 dataset 中删除
ASK Redirection
在 MOVED 永久重定向提了以下临时重定向
临时重定向,主要在迁移哈希槽过程中使用
迁移过程中,如果客户端执行的 key 在源节点不存在,那么就需要 临时重定向 到新节点来执行(没有必要在源节点执行,反正最终都要迁移到新节点)
源 Cluster 节点在收到一个 key 后,检查对应的 hash slot,如果这个 hash slot 不是由当前节点负责,那么直接发送 MOVED,否则:
- 如果这个 hash slot 正在迁移,那么检查这个 key 是否是新 key:
- 如果是新 key,那么 临时重定向 到新的节点
- 否则正常返回
- 否则正常返回
临时重定向,就是发送一个 ASK message 给客户端,将请求临时重定向到新的节点
为什么不直接使用 MOVED 重定向?
Why can’t we simply use MOVED redirection? Because while MOVED means that we think the hash slot is permanently served by a different node and the next queries should be tried against the specified node. ASK means to send only the next query to the specified node.
在迁移哈希槽的过程中,源节点负责的 hash slots 暂时还没有发生改变,如果发送 MOVED message,那么客户端更新映射缓存,后续请求旧 key 就会跑到新的节点,但是 迁移可能还没有完成,如果还要正确执行:
- 再重定向到源节点
- 或者等待迁移完毕
无论哪种方式,效率都很低
客户端连接和重定向处理
前面已经基本将客户端连接和重定向处理到过程介绍了,这里再总结一下:
- 客户端首次执行命令,由于映射缓存为空,往往会收到 MOVED 重定向,这时,可以将映射关系缓存到本地
- 以后执行命令,先计算 key 的 hash slot,然后查缓存获取目标 cluster node,最后执行请求
- 但缓存可能部分过期(集群由于某些原因发生了 Reshard),那么请求可能有三种情况:
- 当前请求的 key 对应的 hash slot 没有迁移,正常执行
- 当前请求的 key 对应的 hash slot 正在迁移:
- 如果是新 key,那么收到 ASK 重定向
- 否则正常执行
- 当前请求的 key 对应的 hash slot 迁移完毕:收到 MOVED 重定向,更新缓存,重新执行请求
Redis Cluster 如何处理读写请求的分发
Normally replica nodes will redirect clients to the authoritative master for the hash slot involved in a given command
写请求分发到主节点:
在 Redis Cluster 中,所有的写操作(如 SET, DEL, HSET 等)必须 由负责该键哈希槽的 主节点 处理。如果客户端尝试向从节点或错误的主节点发送写请求,它将收到一个 MOVED 重定向错误,指示正确的主节点地址。客户端需要重定向请求到指定的主节点。
读请求分发到从节点:
与写请求一样,读请求(如 GET, HGET 等)默认情况下也是发送到主节点
假设主节点为 A,A 的从节点为 B,假设 key0 对应的 hash slot 由 A 管理
如果客户端向 B 发送一个读请求,B 会回应一个 MOVED 重定向错误,将客户端重定向到 A
但在 Redis Cluster 中可以设置从节点进行读取操作,以此来分担主节点的读取压力。
however clients can use replicas in order to scale reads using the READONLY command.
READONLY tells a Redis Cluster replica node that the client is willing to read possibly stale data and is not interested in running write queries.
要实现这一点,客户端可以使用 READONLY 命令通知从节点接受读请求。一旦进入只读模式,客户端就可以向该从节点发送读请求,读取存储在该节点的数据。
当客户端给从节点发送了 READONLY 命令后,从节点之后再收到读请求,只要这个 key 对应的 hash slot 由自己的 master 负责,那么就不会重定向客户端的请求,而是自己处理,降低 master 的压力
注意:Redis Cluster 没有提供读请求的负载均衡(即将读请求均分到不同的从节点执行)
这意味着:如果要实现读请求的负载均衡,需要由客户端自己实现
实现方式也很简单:
- 客户端可以在建立连接时,获取整个集群的状态(master 有哪些,其下的 slave 有哪些)
- 然后可以实现不同的负载均衡策略,如轮询、分片等等,将请求路由到对应的从节点
当然,在从节点执行读请求,会遇到数据不一致的问题,这个就要看你的业务是否有强一致性需求了
错误忍受(Fault Tolerance)
心跳包(Heartbeat Packet)
为了检测整个集群的状态,节点间会定期地互相发送心跳包(Heartbeat Packet)
Redis 集群的节点通过发送和接收 ping 和 pong 包来不断交换信息,这两种包的结构相同,携带重要的配置信息,唯一的区别在于消息类型字段。我们将 ping 和 pong 包的组合称之为心跳包。
心跳包包含以下内容:
- 类型:是 ping 还是 pong
- Node ID
- RESP 的 ip + port
- Cluster bus 的 ip + port
- 版本号
- 当前节点的身份信息
- 包含的哈希槽
- 如果是从节点,还会记录主节点的 Node ID
- 发送节点视角下的集群状态信息(包括 down 和 ok)
简单来说,就是包含了节点本身的元数据,以及发送节点视角下的集群状态信息
这里详细说一下 发送节点视角下的集群状态信息,对于后面理解 Redis Cluster 的错误检测会有帮助:
当一个节点发出心跳包时,它会在包里面包含它所观察到的集群状态的信息。这有助于其他节点获得关于集群健康状况的信息,比如:
- 下线状态(down):如果发送心跳包的节点观察到集群或者特定的节点出现了问题(比如无法达到或不再发送心跳信号),它会在心跳包中报告该节点或集群处于 down 状态。
- 正常状态(ok):相反,如果发送心跳包的节点认为集群状态良好,所有节点都是活跃的并且响应心跳信号,那么它会报告集群状态是 ok 的。
这样的设计能让集群中的其他节点根据接收到的心跳信息来更新自己的状态视图,从而使整个集群能够对节点失效做出快速响应,并相应地进行故障转移或重组。
发送机制
- 每个节点每秒会 随机 ping 一些节点,这样每个节点发送的 ping 包数(及接收到的 pong 包数)是一个恒定的量,与集群中的节点数量无关。
- 每个节点都要确保 ping 那些超过一半的超时时间(NODE_TIMEOUT)还没有发送 ping 或接收 pong 的其他节点。在 NODE_TIMEOUT 时间到期之前,节点还会尝试重新连接 TCP 链路,以确保节点不因为当前 TCP 连接的问题而被认为是无法到达的。
举个例子:
在一个有 100 个节点的集群中,如果节点超时时间设置为 60 秒,每个节点会尝试在 30s 内发送 99 个 ping 包,那么每秒就要发送 3.3 个 ping 包,整个集群 100 个节点,那么每秒就会产生 330 个 ping 包
虽然看起来很多,但是这些包都是均匀的分配到每一个节点,不会造成太大的负担
错误检测
Redis 集群使用故障检测来识别当一个主节点或副本节点无法被集群大多数节点访问时的情形,并进行相应处理,例如提升一个副本成为新的主节点。如果无法执行故障转移(没有可用从节点),集群将进入错误状态,停止接收客户端查询。
节点会保存与其他节点相关的一系列标志。用于故障检测的有两个标志,称为 PFAIL(可能的故障)和 FAIL(确认故障)。PFAIL 是一个未被确认的故障类型,而 FAIL 意味着节点发生故障,并且这种状况已经被集群中大多数主节点在固定时间内确认。
当节点超过 NODE_TIMEOUT 时间无法访问时,其他节点会给该节点标记 PFAIL。 无论是主节点还是副本节点,都可以为其它类型的节点标记 PFAIL。Redis 集群中节点不可达的概念是指我们发送了 ping,但在 NODE_TIMEOUT 时间内还未收到回复。
一个节点单独的 PFAIL 标志只是该节点关于其他节点的本地信息,不足以触发故障转移。要视为节点已经 down 掉,需要将 PFAIL 状态升级为 FAIL。
那么如何将 PFAIL 状态升级为 FAIL?
升级需要满足三个条件:
- 某节点(称为 A)将另一个节点(称为 B)标记为 PFAIL。
- 通过心跳检测机制,A 获取到了其它主节点对于 B 是否为 down 的意见
- 大多数的 有效(在
NODE_TIMEOUT * FAIL_REPORT_VALIDITY_MULT内报告 PFAIL 或者 FAIL 状态) 意见都认为这个节点为 down
那么:
- 节点 A 将 B 标记为 FAIL
- 给其它节点发送 FAIL message
FAIL message 会强制其它节点将 B 标记为 FAIL
从节点选举和升级过程
当一个主节点被标记为 FAIL,并且有可用的从节点,那么故障转移可以进行
故障转移的过程是这样的:
首先,每个从节点都是新的主节点的候选者
从节点会递增 currentEpoch(投票轮数)
每个从节点会通过 cluster bus 发送 FAILOVER_AUTH_REQUEST 包,请求其它主节点给自己投票
每个主节点在 NODE_TIMEOUT * 2 时间内,只有一次投票机会(防止多个从节点当选),当主节点收到 FAILOVER_AUTH_REQUEST 包后,如果有投票机会,就会给这个从节点投票(发送 FAILOVER_AUTH_ACK)
从节点会 抛弃 不属于当前 currentEpoch 的投票
当一个从节点收到大多数主节点的投票后,它就成为了新的主节点
如果超过 NODE_TIMEOUT * 2 时间,还没投票完毕,本轮投票失败,等待 NODE_TIMEOUT * 4 开启新的一轮投票
一旦选举出新的主节点,其他节点会被通知这一变更,确保整个集群中所有节点的配置信息保持一致。
主节点重新加入集群的过程
A master node will change its configuration to replicate (be a replica of) the node that stole its last hash slot.
当一个主节点因为某些原因(例如网络分区或者服务崩溃)丢失了其所有的哈希槽,并且这些哈希槽被集群中的其他主节点接管之后,该节点在重新加入集群时将不再担任之前的主节点角色。
相反,它将更改其配置,成为接管了它 最后一个哈希槽的那个节点的副本
In general it may happen that A rejoins after a lot of time, in the meantime it may happen that hash slots originally served by A are served by multiple nodes, for example hash slot 1 may be served by B, and hash slot 2 by C.
副本迁移(Replica migration)
Intro
在 高可用 这里简单提了一下副本迁移的好处
假设这种情况:
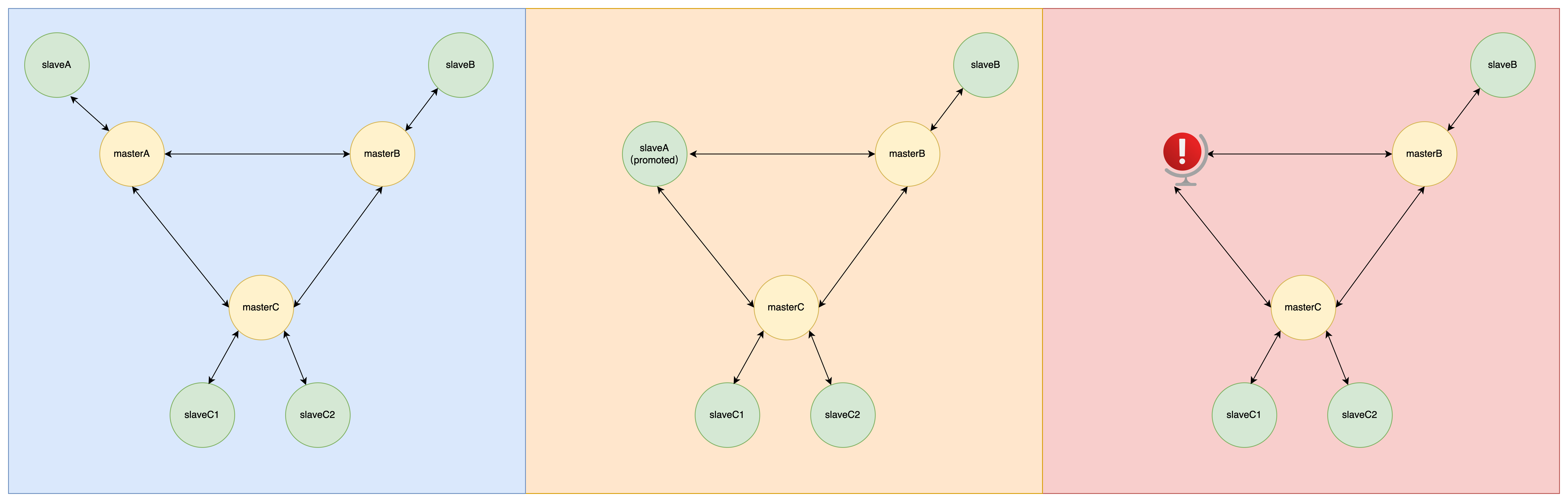
- master A 挂了,故障转移,slave A 成为新的主节点
- slave A 也挂了,没有副本可用,整个集群服务不可用
为了进一步保证可用性,引入了「副本迁移」机制
如果一个主节点没有任何子节点,我们将其成为孤儿主节点
当集群中出现孤儿主节点,副本迁移机制就起作用了,它会将某一个主节点冗余的丛节点迁移到孤儿主节点,使其成为孤儿主节点的从节点:
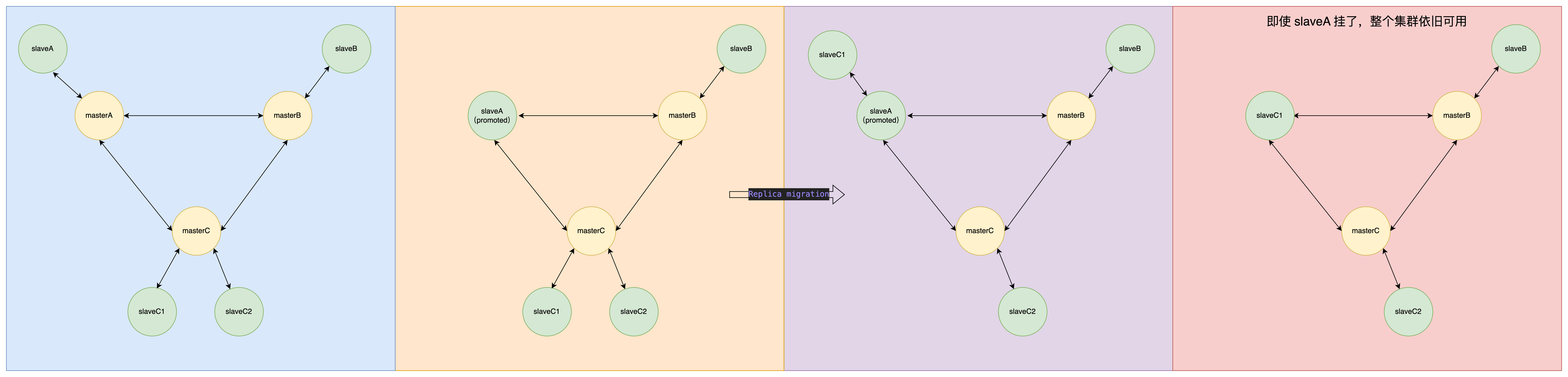
- master A 挂了,故障转移,slave A 成为新的主节点
- 由于 slave A 为孤儿主节点,执行副本迁移,将 slaveC1 迁移,作为 slave A 的从节点
- slave A 也挂了,故障转移,slave C1 成为新的主节点,集群仍然可用
Algorithm
副本迁移的基本算法如下:
- 当一个从节点检测到集群中出现至少一个孤儿主节点,开始尝试副本迁移
- 发现孤儿主节点的从节点可能有很多,但采取行动的从节点只有一部分
- 采取行动的从节点是:从节点数量最多的主节点中,不处于 FAIL 状态且节点 ID 最小的从节点。
举个例子:
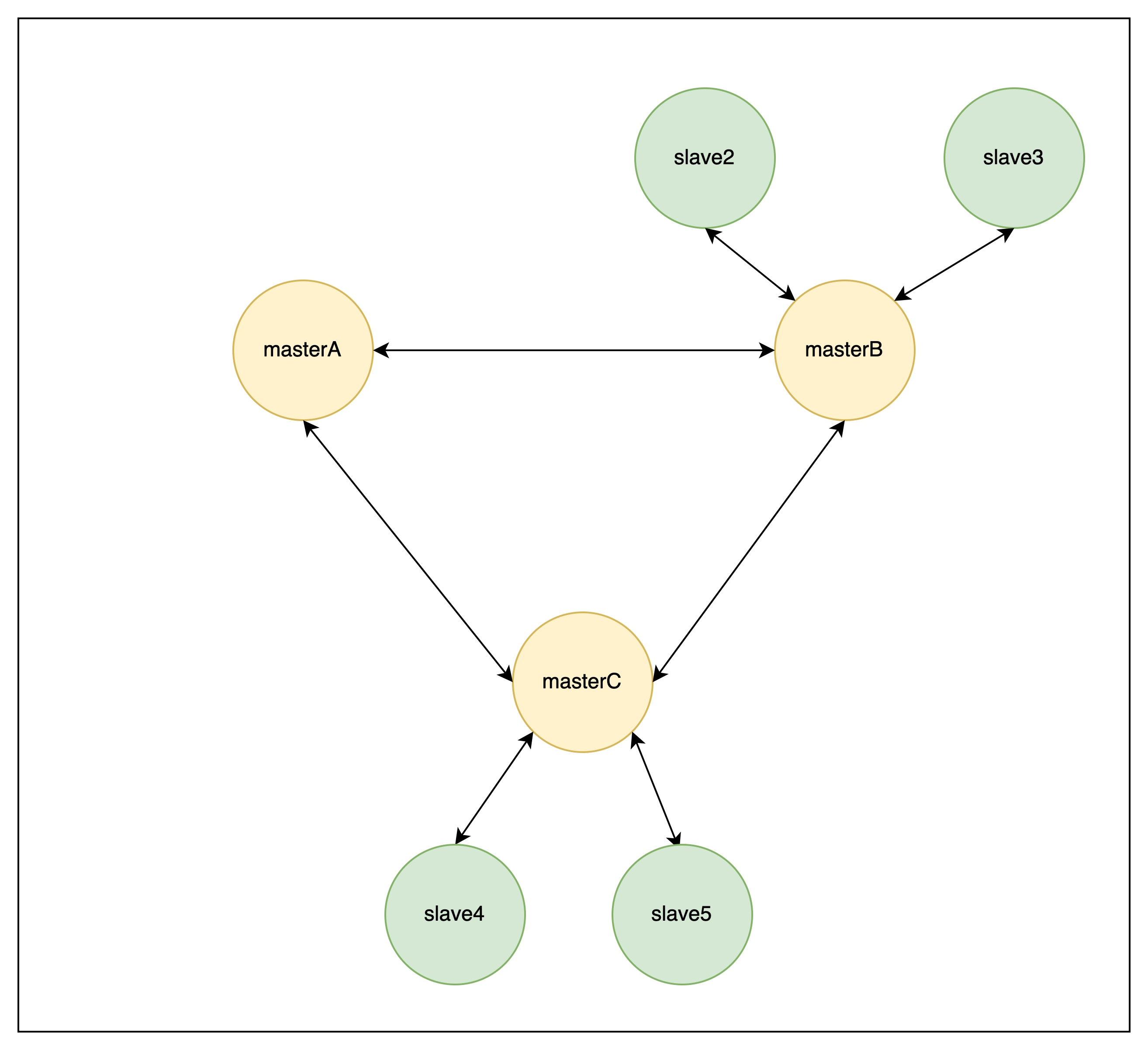
如果上面的节点都不是 FAIL 状态,那么会执行迁移过程的从节点为 slave2
可以通过配置 cluster-migration-barrier 来限制每个主节点最少具有的不处于 FAIL 状态的从节点数量